reactive lymph node ultrasound
 Reactive vs malignant lymph nodes (ultrasound features) | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org
Reactive vs malignant lymph nodes (ultrasound features) | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.orgWhat are the reactive lymph nodes? Synopsis You've probably had swollen glands at some point in your life, like when you've had a cold or other infection. The swollen glands are actually, which are often reactive lymph nodes. You can also hear this condition called reactive lymphadenopathy. You have groups of small lymph nodes in the form of beans all over the body. They are located in the neck, in the armpits, in the chest, in the abdomen and in the groin. They are part of the lymph system, which is also part of its immune system. The lymphatic system helps combat infections and prevent them from spreading. Your doctor may use the term "reactive lymph nodes" when examining it for swelling or mass. If you have a dough, you can also see a reference to the reactive lymph nodes when you review the results of the lab. This means that your lymph nodes are reacting to something that's happening in your body. However, it is generally not a reaction to anything serious. In fact, reactive lymph nodes are harmless. Reactive lymph nodes are not caused by an infection or cancer within the lymph node itself. Read more about reactive lymph nodes, what causes them and when to worry. Usually, you can't feel your own lymph nodes. When they are swollen or reactivated, however, you may feel them when you press your hands against your skin. They could feel as small as a pea or as big as a golf ball. It could even be able to see swelling in the neck, armpits or groin. Note that you may have reactive lymph nodes in multiple areas of the body. In addition to swelling, you can feel the following when you touch the lymph nodes: Depending on the underlying cause, you can also have a range of other symptoms. If the lymph nodes are responding to a higher reparatory infection, for example, it may have a spongy nose, sore throat or fever. Swollen lymph nodes may occur in a single area of the body or in multiple places. Reactive lymph nodes are a sign that your lymph system is working hard to protect it. Lymph fluid accumulates in lymph nodes in an effort to catch bacteria, viruses, or other harmful pathogens. This helps prevent the infection from spreading to other parts of the body. They also sometimes occur as a result of a , such as lupus. These are conditions that involve your immune system by wrongly attacking the tissues of our body. In addition, children experience reactive lymph nodes when they come into contact with new germs throughout childhood, even if they do not have an infection. Some common bacterial or viral infections that can cause reactive lymph nodes include: Other causes are: The location of reactive lymph nodes can help reduce the cause. For example, swollen lymph nodes in the neck may be due to a higher respiratory infection. A dental infection could cause swollen lymph nodes around the jaw. HIV, mononucleosis and immune system disorders can lead to swollen lymph nodes throughout the body. Swated lymph nodes are caused by cancer. When they are, it is usually related to or, that both involve the lymph system. However, enlarged lymph nodes can also be a sign that other types of cancer, such as , have spread (metasified) to lymph nodes. Make an appointment with your doctor if you notice that your lymph nodes feel difficult or unmovable. Reactive lymph nodes are usually a symptom of an underlying infection, so your doctor will start asking about your other symptoms and taking your vital signs. They may also feel their lymph nodes and ask if they experience any pain or sensitivity while doing so. Depending on your symptoms and what you encounter during a physical exam, you can also order a blood test or imaging test, such as an MRI scan. They can also decide on a lymph node. This involves using a needle to take a sample of small tissue and analyze it to detect signs of cancer. If you have cancer, this can also help your doctor determine if you spread. Swollen lymph nodes often do not need treatment. Some minor viral infections, such as flu, have to run their course. Viral infections cannot be treated with antibiotics. To help with painful or tender lymph nodes while healthy, try: Other infections, such as bacterial infections, may require antibiotics or other medicines. If you have an autoimmune condition or cancer, your treatment options will depend on the type and stage of your condition. Reactive lymph nodes are usually just a sign that your immune system is doing its job in fighting an infection. They should go down in size while you're healthy. If you feel tough or do not seem to be shrinking back to your usual size as your disease resolves (usually within a week or two), contact your doctor. Last medical review on May 9, 2018Read this following

Ultrasound image of reactive axillary lymph node. | Download Scientific Diagram
Lymphadenopathy - Wikipedia

Reactive groin lymph node | Radiology Case | Radiopaedia.org
Hong Kong Journal of Paediatrics [HK J Paediatr (New Series) 2009;14:29-36]

Ultrasound of malignant cervical lymph nodes. - Abstract - Europe PMC

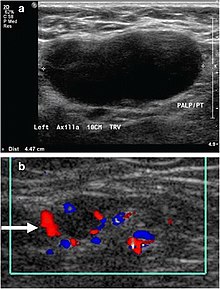
Reactive axillary lymph node | Radiology Case | Radiopaedia.org

PDF) Ultrasonography of superficial lymph nodes: Benign vs. malignant

Mistakes in ultrasound diagnosis of superficial lymph nodes
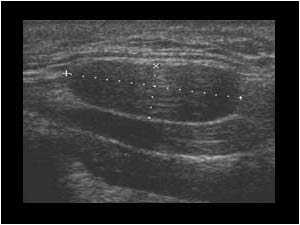
4.4.1 Benign lymph nodes | Ultrasound Cases

Typical US appearance of lymph nodes: typical reactive node image (a)... | Download Scientific Diagram

Ultrasonographic Differentiation of Benign From Malignant Neck Lymphadenopathy in Thyroid Cancer - Kuna - 2006 - Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine - Wiley Online Library
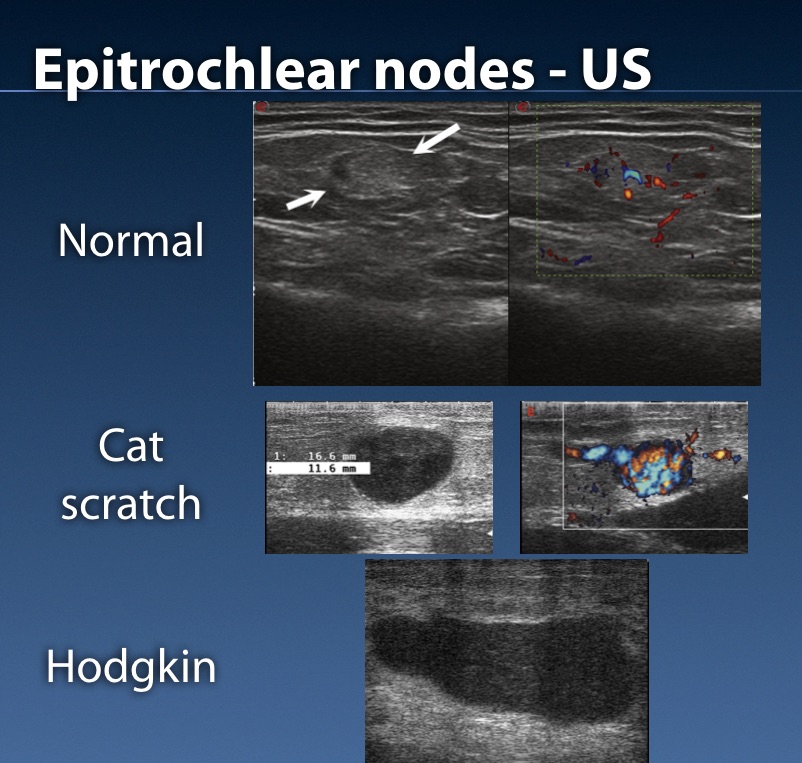
Lymph Nodes

Typical US appearance of lymph nodes: typical reactive node image (a)... | Download Scientific Diagram

Ultrasound of malignant cervical lymph nodes. - Abstract - Europe PMC
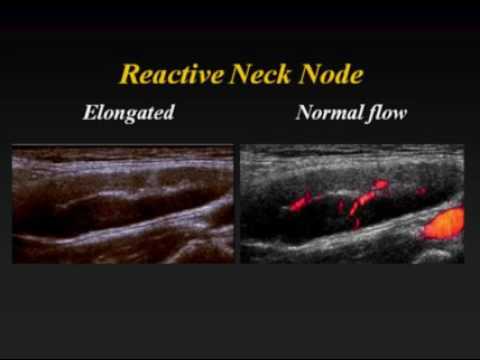
Ultrasound of Cervical Lymph Nodes - YouTube
Axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer patients: sonographic evaluation

Lymph node enlargement | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org
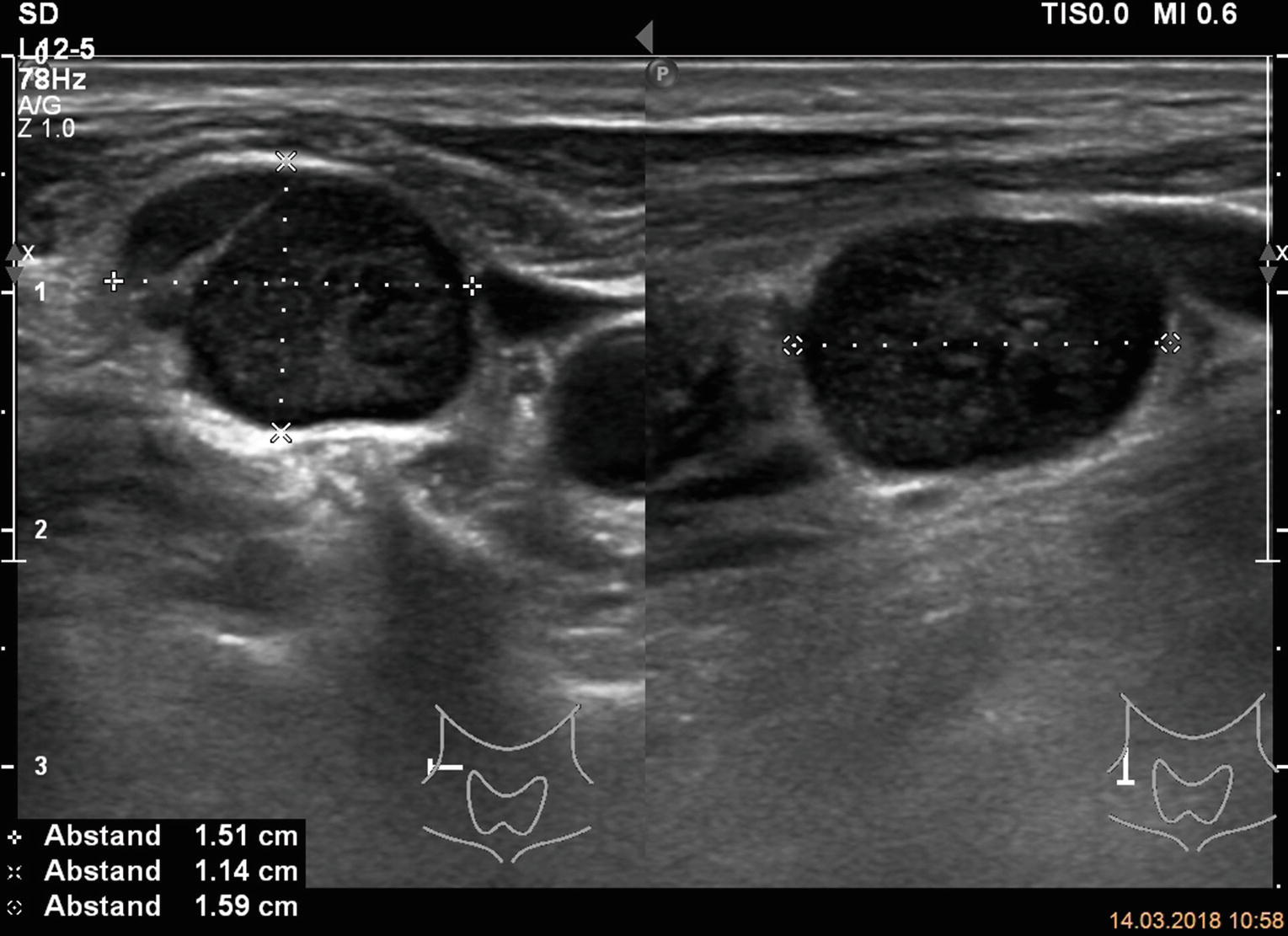
Sonography of Lymph Nodes in the Neck | SpringerLink
Hong Kong Journal of Paediatrics [HK J Paediatr (New Series) 2009;14:29-36]
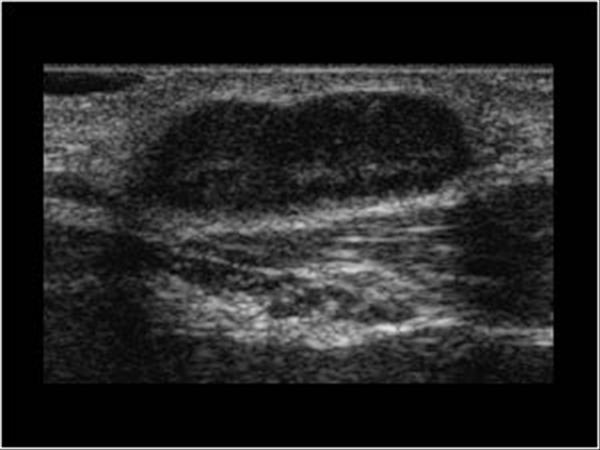
Head and Neck | 4.4 Lymph nodes : Case 4.4.2 Malignant lymph nodes | Ultrasound Cases

Lymphadenopathy - Wikipedia
Ultrasound findings of the physiological changes and most common breast diseases during pregnancy and lactation

Objectives
Hong Kong Journal of Paediatrics [HK J Paediatr (New Series) 2009;14:29-36]
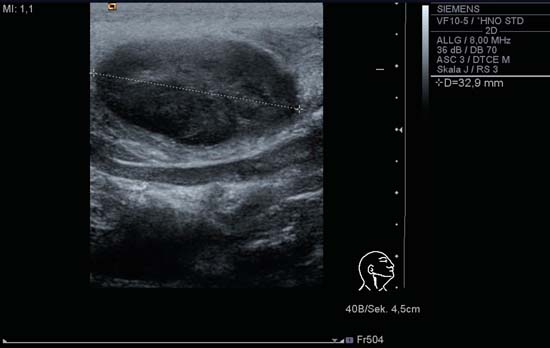
Neck Lymph Nodes | Radiology Key
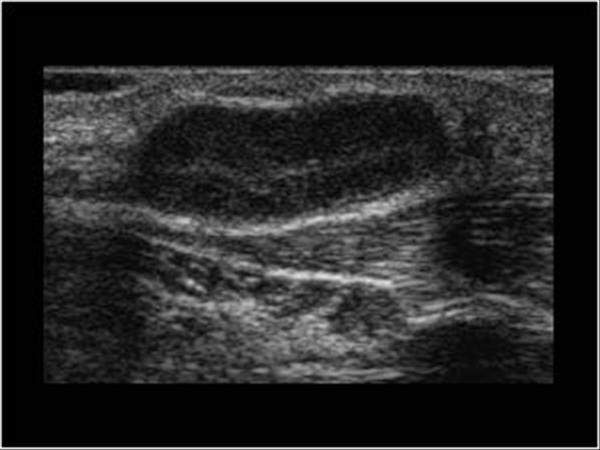
Head and Neck | 4.4 Lymph nodes : Case 4.4.2 Malignant lymph nodes | Ultrasound Cases

Can ultrasound elastography distinguish metastatic from reactive lymph nodes in patients with primary head and neck cancers? - ScienceDirect

Chapter 5 Ultrasound Characteristics of Benign vs Malignant Cervical Lymph Nodes - ScienceDirect

an inguinal ultrasound examination showed subcutaneous edema and... | Download Scientific Diagram
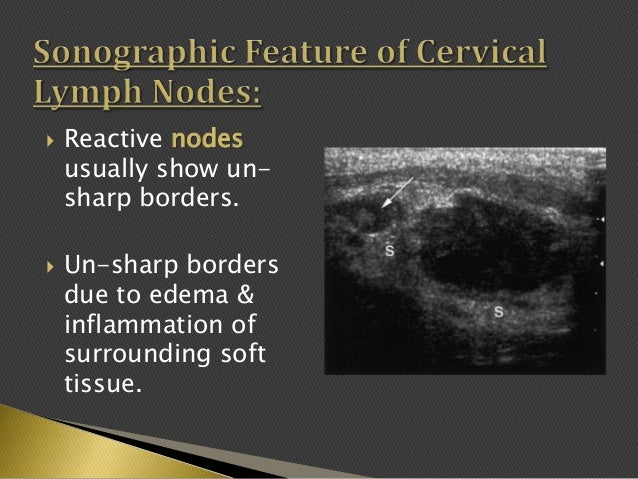
Imaging of enlarged lymph node

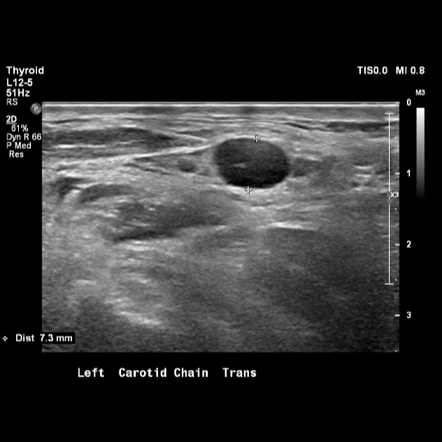
Thyroid Cancer And Hashimoto's 101: Less Cancer Lymph Nodes and More Reactive Ones – Thyroid Center of Santa Monica
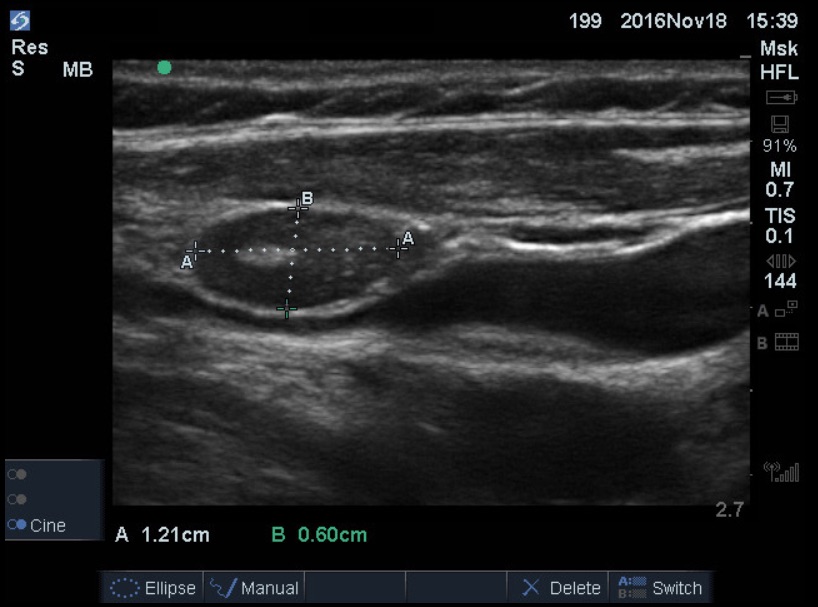
Lymph Nodes
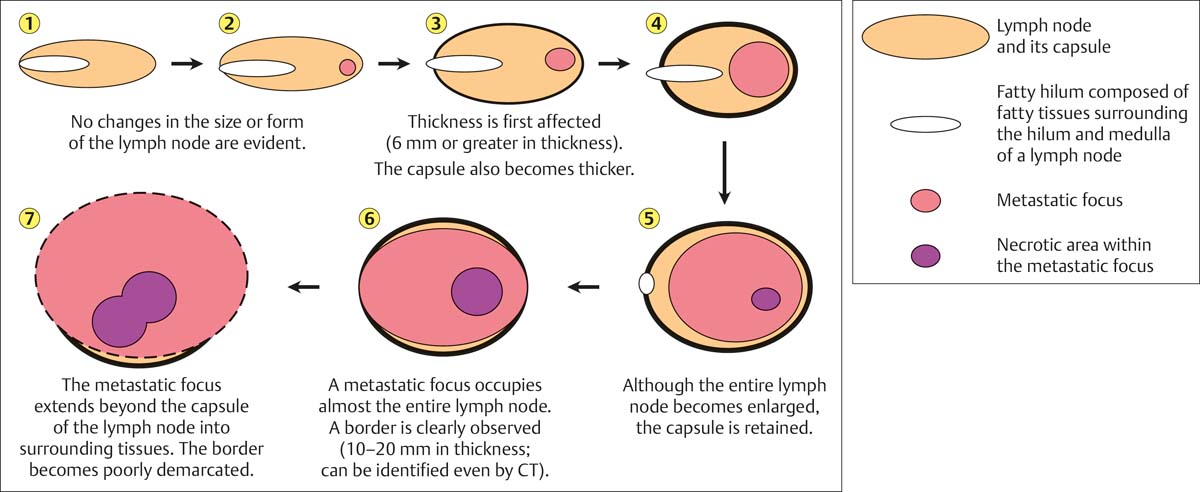
Neck Lymph Nodes | Radiology Key
Hong Kong Journal of Paediatrics [HK J Paediatr (New Series) 2009;14:29-36]
The Radiology Assistant : Neck Masses in Children
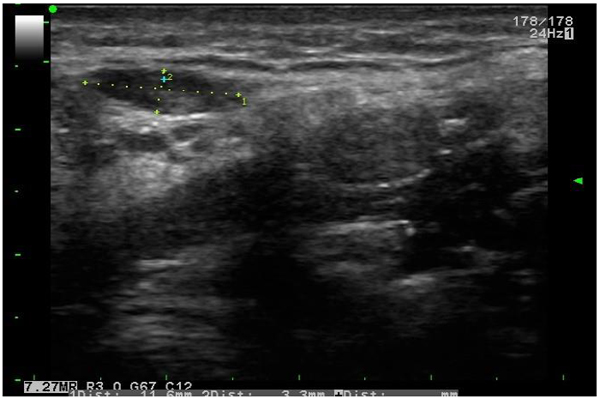
Ultrasonographic Appearances of Cervical Lymph Nodes in Healthy Turkish Adults Subpopulation: Preliminary Study ~ Fulltext

Can ultrasound elastography distinguish metastatic from reactive lymph nodes in patients with primary head and neck cancers? - ScienceDirect
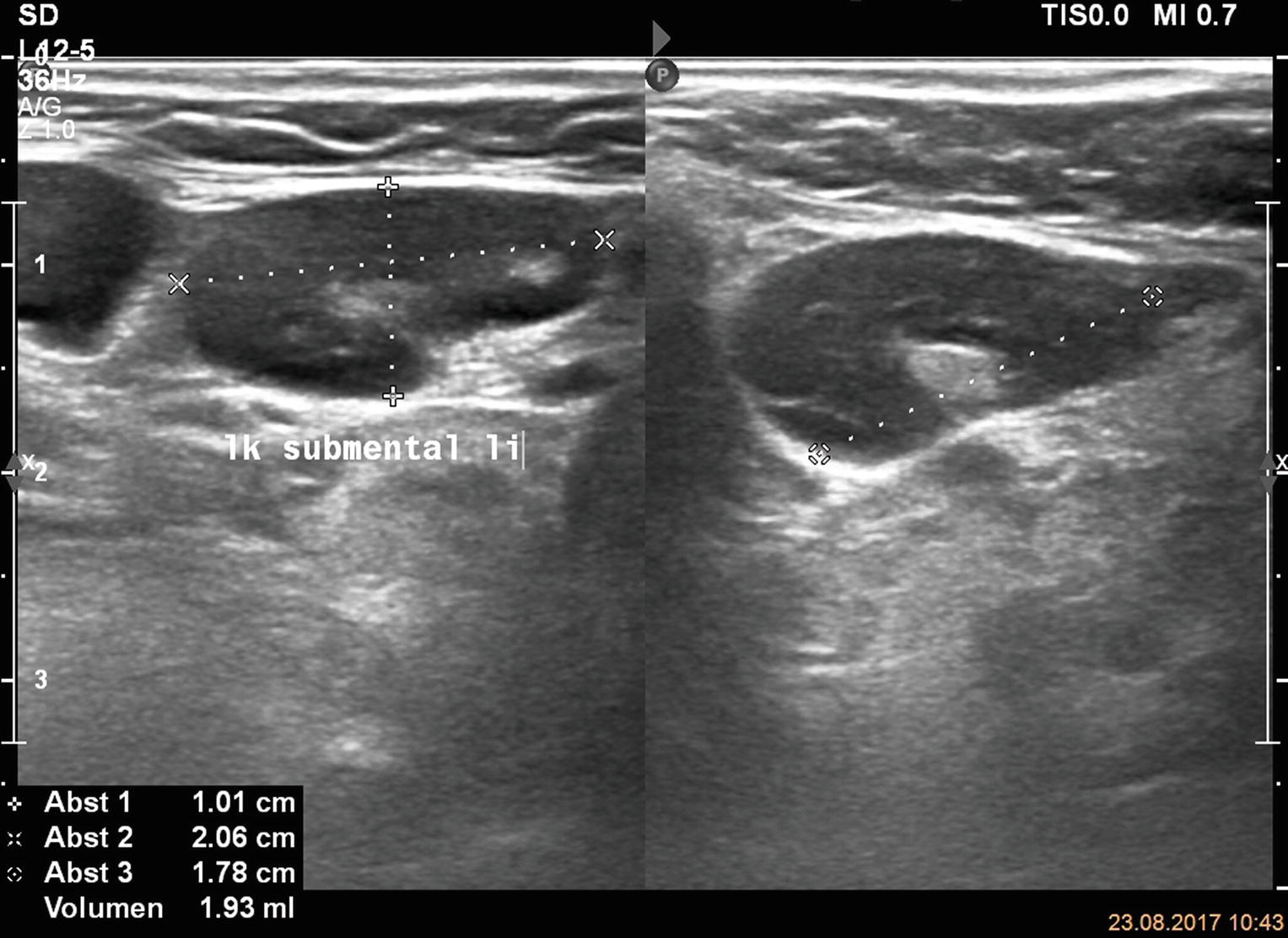
Sonography of Lymph Nodes in the Neck | SpringerLink
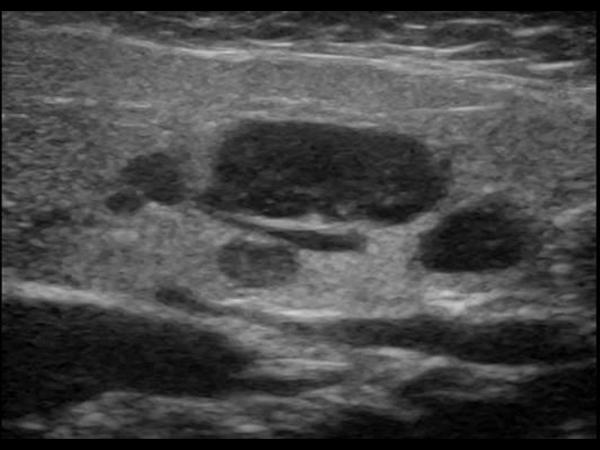
Head and Neck | 4.3 Salivary glands : Case 4.3.7 Salivary gland pitfalls | Ultrasound Cases
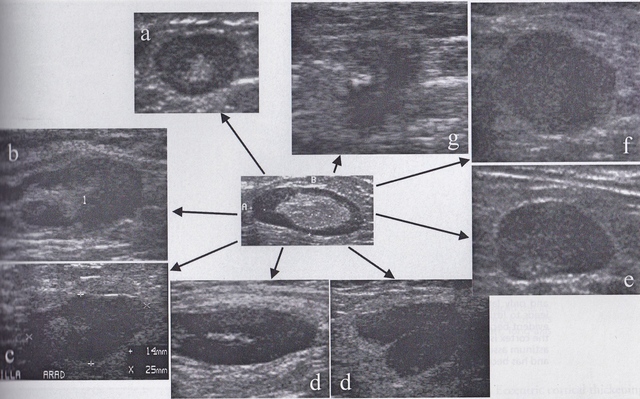
Breast Cancer Topic: Lymph Nodes on Ultrasound
Posting Komentar untuk "reactive lymph node ultrasound"